Patterson’s Mistake: the Battle of Lake Borgne Revisited
December 30, 2014 in American History, general history, History, Louisiana History, Nautical History
American Commodore Daniel T. Patterson made the single biggest mistake of the Louisiana portion of the War of 1812 when he deployed almost all of his naval force to patrol and spy along the coastal area of Lake Borgne in December 1814 while he remained in New Orleans. His tactical error not only gave the British control of Lake Borgne during their invasion, it also gave them the light draft American ships to move their troops as quickly as possible over the wide expanse of the lake to a disembarkation point at Pea Island, some 60 miles above where the British warships were anchored.
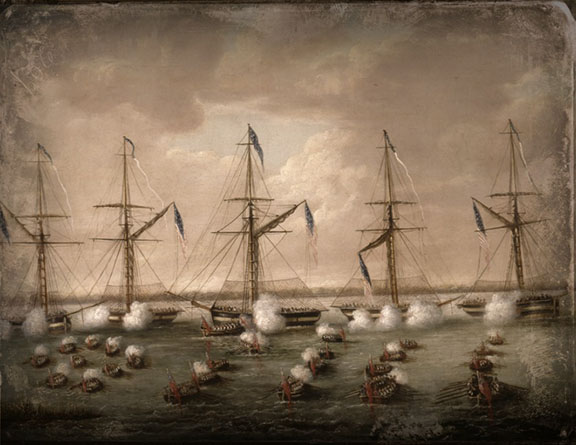
On the morning of Dec. 14, 1814, American Lieut. Thomas ap Catesby Jones regarded with both trepidation and elation the three columns of armed British rowboats full of men pulling towards Jones’ fleet of five American gunboats lined up at the entrance to Lake Borgne near Malheureux Island. He had carefully picked his position to line up the light draft gunboats to use their broadsides to best effect, but the tides and wind had betrayed the Americans’ best efforts, and some were pulled somewhat out of formation, and Jones’ flagship Gunboat No. 156, along with another, had grounded for the second time and was mired on the bottom: there was no way to shift position, or continue to retreat to the safety of the fortification guns at Petite Coquilles: they would have to fight off the British where they were.
Even though Jones and his 181 men were outnumbered nearly seven to one by the 1,200 advancing British in 42 armed longboats, Jones was eager to take them on and merit the post captain promotion he would surely deserve for such a feat. He was young and impetuous, qualities which his commander, Patterson, utilized to the fullest extent. Patterson had instructed him to “sink or be sunk” in a possible confrontation with the British, and he didn’t intend to let any of his five gunboats go down.
It must have unsettled Jones when the British fleet’s commander, Nicholas Lockyer, halted the rowboats just out of gun range so all his men could enjoy an early lunch before the assault after having rowed 30 miles from their ships. Lockyer, commodore of HMS Sophie, was a seasoned British commander and knew the value of psychological, as well as tactical, battle strategy. When lunch was over, and the men fortified, he ordered the fleets to renew rowing toward the gunboats. All the British were chanting “Give Way!” and cheering as boisterously as they could while the single carronades mounted at the bows of each of their boats fired intermittently at the gunboats, with Jones’ No. 156 flagship being targeted first.
“The Americans being moored in line, at least four hundred yards apart from one other, the attacking boats were a good deal divided, and each boat pulling away wildly came to close quarters,” wrote Capt. Cooke in his “Narrative of the British Attack on New Orleans.” “The clouds of smoke rolled upwards, and the splashing of round and grape shot in the water, and the loud exhortations of “Give way!” presented an animated scene at mid-day.”
“Capt. Lockyer, in the barge of the Seahorse, was first up to the mark (Jones’ 156), and his boat’s crew were most uncourteously handled by the American commodore, who at first would not let Capt. Lockyer get aboard, and a rough tussle took place, but other boats coming up, the sailors, sword in hand, being covered by the fire from the small arms of the marines, cut away their defensive netting that was coiled round her decks like a spider’s web,” continued Cooke.
“The British at last mastered the Americans, and captured all the five vessels in succession, making their different crews prisoners, but not before some of the guns of the captured vessels had been turned upon those that still resisted, to enable the boarders to complete their victory.”
Leading his men on the boarding assault on No. 156, Lockyer suffered three wounds, at least one of a severe nature, and Jones, too, was severely wounded when a musket ball slammed into his left shoulder early in the boarding fray. He was taken below and replaced by his second in command, Masters Mate George Parker, who also fell wounded during the hand to hand combat that ensued.
When the British took control of No. 156, its guns were brought to bore on No. 163, and the rest in succession soon fell like a line of tipped over dominoes.
The whole battle took less than two hours. Both commanders were injured severely, and the battle took a significant toll on both sides. The Americans lost 10 killed in action, 35 wounded, with 86 captured, and the British had 17 killed in action, with 77 wounded in action. The wounded were evacuated, and the British renamed the gunboats HMS Ambush, Firebrand, Destruction, Harlequin and Eagle. They proceeded to use the gunboats to speed up transportation to their disembarkation point of Pea Island, 30 miles further up Lake Borgne, near the mouth of the Pearl River.
In his Dec. 16, 1814, letter to John Wilson Croker, secretary to the British Admiralty, Vice Admiral Sir Alexander Cochrane had nothing but the highest praise for Lockyer and his men:
“Lockyer had the good fortune to close with the flotilla, which he attacked with such judgment and determined bravery, that notwithstanding their formidable force, their advantage of a chosen position, and their studied and deliberate preparation, he succeeded in capturing the whole of the vessels, in so serviceable a state as to afford at once the most essential aid to the expedition…Our loss has been severe, particularly in officers, but considering that the successful enterprize has given us command of Lac Borgne (sic), and considerably reduced our deficiency of transportation, the effort has answered our fullest expectations.”
Even though he must have been in extreme pain from his wounds, Lockyer managed to write a letter to Cochrane four days later from onboard the HMS Sophie detailing the Lake Borgne operation and commending individual officers:
“After several minutes’ obstinate resistance in which the greater part of the officers and crew of this boat were either killed or wounded, myself amongst the latter, severely, we succeeded in boarding, and being seconded by the Sea Horse’s first barge, commanded by Mr. White, midshipman, and aided by the boats of the Tonnant, commanded by Lieut. Tatnell, we soon carried her, and turned her guns with good effect upon the remaining four…In about five minutes we had possession of the whole of the flotilla.”
Jones and the rest of the captured Americans were taken onboard the HMS Gorgon, later to be transferred to Bermuda. It would be mid March of 1815 before they would be on US soil again. Jones faced a court of enquiry upon his return, but passed it with flying colors for his bravery and courage, thanks to the afterglow of the Battle of New Orleans.
The British victory led by Lockyer was an American disaster, as following it, Gen. Andrew Jackson had no lookouts or defenses on Lake Borgne, plus there was no defensive gunpower to hold the forts on the Rigolets and Bayou St. Jean. It is likely things would have happened much differently with the ensuing battles if the crew of the tender USS Sea Horse had not escaped capture after blowing up their supply ship on its way to get stores from Bay St. Louis, not long before Lockyer and company successfully took the five gunboats. Capt. William Johnson from the US tender, after observing the gunboats’ battle from a tree, traveled quickly to Patterson in New Orleans to tell him of the advancing British, as he knew about it within a day after it had occurred, while the British were still laboriously transporting men, guns and supplies to Pea Island, using their seized gunboats. Patterson relayed the bad news to Gen. Andrew Jackson, who must have been absolutely livid, considering he knew full well that now he had no eyes at all on the British and was, for all intents and purposes, blind.
Patterson’s small navy had been reduced to the Carolina schooner and Louisiana sloop, both at New Orleans, and one gunboat at Ft. St. Phillip on the Mississippi River. Six fast armed schooners taken in the Patterson-Ross raid of Jean Laffite’s Barataria sat idle at the Navy yard in New Orleans, but couldn’t be used for two reasons: there were no sailors to man them, and they were still awaiting judgment in admiralty court, so it was like they weren’t even there. The Louisiana also couldn’t be used initially due to a lack of men. Only the Carolina boasted a full crew of New Englanders who had arrived with the ship in August 1814. Patterson’s unpopularity with sometime privateer crews made him anathema for them to want to work for his navy.
In “The Amphibious Campaign for West Florida and Louisiana 1814-1815,” historian Wilburt S. Brown, retired Marine Corps major general, said the Lake Borgne battle was a “classic example of an operation in which the defenders were almost stripped of naval strength before the operation was begun, while the attackers’ naval strength remained overwhelming.”
Patterson’s mistake began early in December, shortly after Jackson’s arrival in New Orleans, when the five gunboats and tender Sea Horse were sent into the waters around Pass Christian to watch for British ships and movements. Jones had dispatched two of the gunboats, No. 23, and 163, under command of Isaac McKeever and Sailing Master Robert Ulrick, toward Dauphin Island to provide an early warning. Those two gunboats spied the British fleet advancing, and fired a shot or two off at the HMS Armide (Vice Admiral Cochrane’s flagship) and HMS Seahorse before darting into the shoals and racing back to the other three gunboats near Ship Island to sound the alarm. The Armide gave chase, then could not pursue due to almost grounding; Jones’s No. 156 grounded temporarily, but he managed to get it free overnight with the next tide. In the meantime, the British tried to capture the US Sea Horse supply tender only to be stymied when her captain blew her up. They then proceeded with the barges (longboats) against the US gunboats.
McKeever and Ulrick behaved somewhat irresponsibly in firing at the massive fifth rate British ships, as the chase that followed drew the invading fleet’s attention to the whole gun boat group near the lower opening of Lake Borgne. The gunboats were only supposed to spy on the British movements, then retreat en masse back to the coverage of the fort at Petite Coquilles. It is unknown if Jones gave them instructions to fire. The schooner-rigged gunboats, popularly known as “Jeffs,” were known as poor sailing vessels even though they only drew five feet of water. Their main advantage was in the shoal waters where the large frigates and other warships could not go, but even there they had to use caution as tricky tides could find them in water barely chest high.
Patterson’s mistake of sending all five gunboats for the spying mission together could easily have been avoided by sending just a few men in light rowboats or the like to watch the coast and report back. Jones also erred when he decided to hold tight and battle a superior force rather than blow up the gunboats so they could not be used by the enemy. The only good achieved by the American side from the Battle of Lake Borgne was the false intelligence the British received from the prisoners regarding the size of Jackson’s army, which they had exaggerated.
Lockyer came out the clear winner of the Lake Borgne contest, but due to his injuries, he missed out on the rest of the campaign. He was not proclaimed out of medical danger (sepsis killed many wounded from infection) until mid-January 1815. He received a promotion from commodore to post captain in 1815 for his service.
Subsequent mistakes made on the British side, plus Jackson’s keen tactical skills and a supply of needed flints and powder to the Americans from the Laffites led to the Jan. 8, 1815 Battle of New Orleans overwhelming victory for the US.
For related articles, see:
The Saga of Melita and the Patterson-Ross Raid at Barataria
The Case of the Spanish Prize Ship at Dauphin Island
The British Visit To Laffite, a Study of Events 200 Years Later




Recent Comments